Paula Loop is Leader of the Governance Insights Center at PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. This post is based on a PwC publication by Ms. Loop and Terry Ward.
Does your board have the right makeup for the future?
Board composition is “the” issue for investors in 2017. Some industries are taking more steps to refresh their board than others—how does yours stack up? As the economic environment changes and lines between industries start to blur, companies are looking for directors with different, less traditional and even broader skills. Technology skills will be key across sectors.
Who’s sitting in your boardroom? Do your directors bring the right mix of skills, experiences and expertise to best oversee your company? Are they a diverse group, or a group with common backgrounds and outlooks? Can they help see into the future and how your industry is likely to take shape? And are some of your directors serving on your board as well as those in other industries?
These questions should be top of mind for executives and board members alike. Why? Because the volume of challenges companies are facing and the pace of change has intensified in recent years. From emerging technologies and cybersecurity threats to new competitors and changing regulatory requirements, companies–and their boards–have to keep up. Some boards have realized that having board members with multiple industry perspectives can prove helpful when navigating the vast amount of change businesses are faced with today.
If your board isn’t thinking about its composition and refreshment, you are opening up the door to scrutiny. Board composition is “the” issue for investors in 2017. Investors want to know who is sitting in the boardroom and whether they are the best people for the job. If they don’t think you have the right people on the board, you will likely hear about it. This is no longer something that is “nice” to think about, it’s becoming something boards “must” think about. And think about regularly.
How can you refresh your board?
In 2016, we analyzed the board demographics of select companies in nine industries to see how they compared to each other and to the S&P 500. Where does your industry fall when it comes to board refreshment? Does your board have the right makeup for the future?
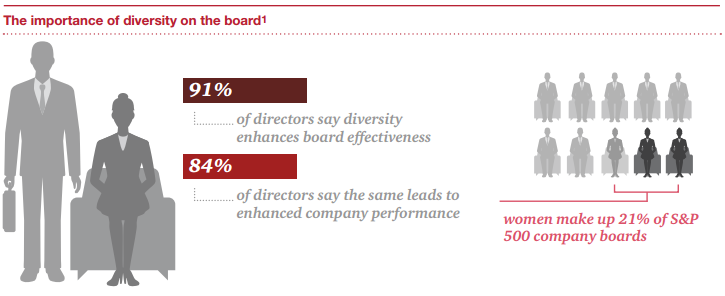
There are a number of ways to refresh your board. One way is to think about diversity. Many have taken on the gender imbalance on their boards and are adding more women directors. But diversity isn’t only about women. It’s about race, ethnicity, skills, experience, expertise, age and even geography. It’s about diversity of thought and perspective. And it’s not just a talking point anymore. Regulators started drafting disclosure rules around board diversity in mid-2016. Whether the rules become final remains to be seen, but either way, board diversity is in the spotlight. Add to that the common criticism that the US is far behind its developed country peers. Norway, France and the Netherlands have been using quotas for a while, and Germany in 2015 passed a law mandating 30% women on the boards of its biggest companies. While it’s unlikely quotas would be enacted in the US, some believe they’re a needed catalyst.
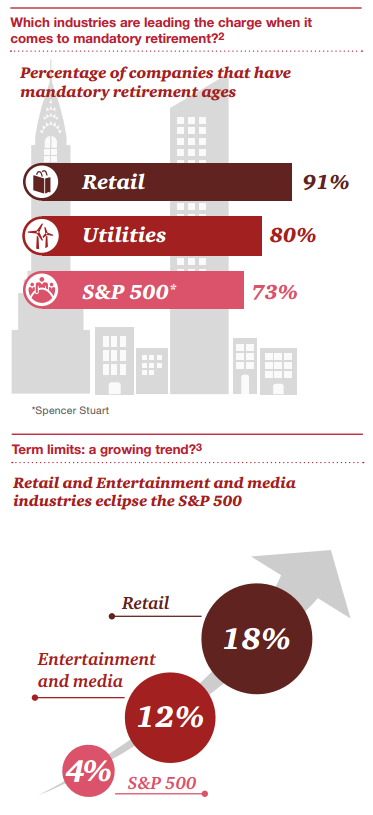
While we only looked at gender diversity on boards, we believe this is a good indicator of the efforts some boards are making to become more diverse overall. Secondly, mandatory retirement ages and term limits are two tools that boards can use to refresh itself. Our analysis showed that some industries seemed to be adopting these provisions more so than others. Some directors question their effectiveness.
Some of the industries in our PwC peer group analysis don’t have term limits at all
- Banking and capital markets
- Insurance
- Communications
- Technology
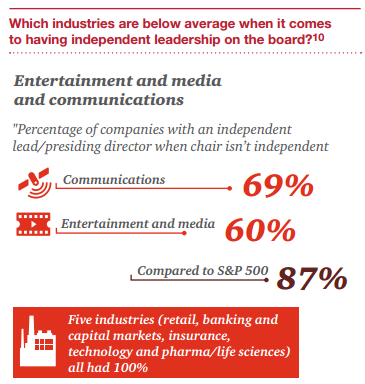
A third move that some companies have taken often, under investor pressure—is to evaluate their leadership structure and split the chair and CEO role. While the issue is still one that investors care about, certain industries have kept the combined role. And some companies don’t plan on making the change any time soon. Most often, boards with a combined chair/CEO role have an independent lead or presiding director. This may ease concerns that institutional investors and proxy firms may have about independence in the leadership role.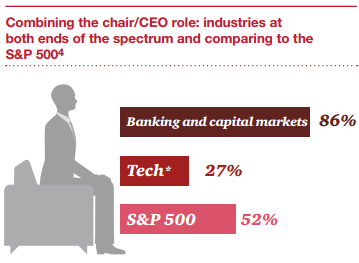
Who would have thought? Some interesting findings
While our analysis shows that most industries didn’t veer too far from the S&P 500 averages for most benchmarking categories, a few stand out. Retail in particular seems to be leading the charge when it comes to board refreshment.
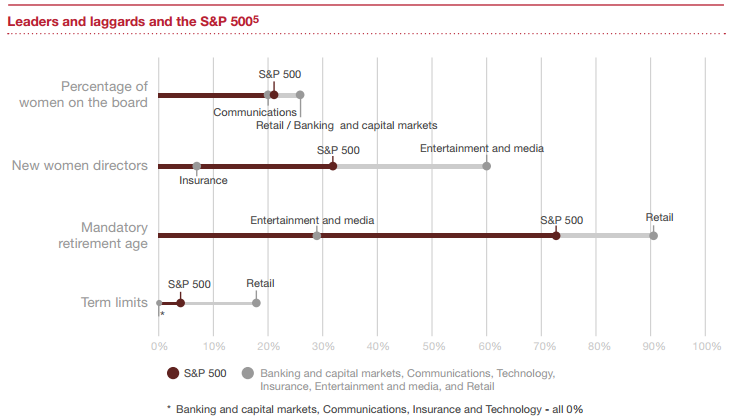
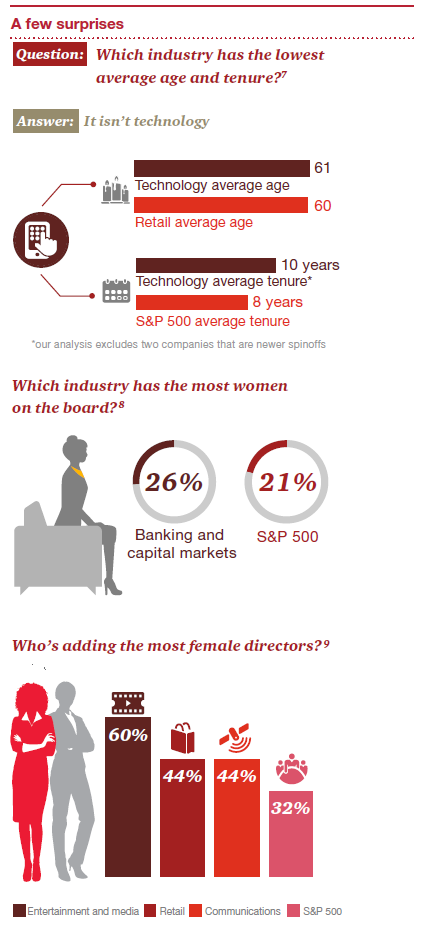
Other industries aren’t moving along quite so quickly. And there were some surprises. Which industry had the lowest average age? Perhaps surprisingly, it’s not technology. Retail claimed that one, too. And, also unexpected, was that technology had one of the highest average tenures. [6] Another surprising finding came from our analysis of the banking and capital markets industry—an industry that’s often considered to be male-dominated. BCM boards had the highest percentage of women, at 26%. That compares to just 21% for the S&P 500. Both the entertainment and media and the communications industries were also ahead of the curve when it comes to women in the boardroom, with the highest and second-highest percentages of new female directors. Retail tied with communications for second-highest, as well.
On a less progressive note, both the entertainment and media and communications industries were below the S&P 500 average when it came to having an independent lead or presiding director when the board chair is not independent. And they ranked lowest of the industries we analyzed on this topic—by far.
Blurred lines across industries
Skills, experience and diversity of thought will likely become even more important in the coming years. In the past five years alone, once bright industry lines have started to blur. Take the retail industry, for example. Brick and mortar stores, shopping malls and strip malls were what used to come to mind when thinking about that industry. Now it’s mobile devices and drones. Across many industries, business models are changing, competitors from different industries are appearing and new skills are needed. The picture of what your industry looks like today may not be the same in just a few years.
Technology is the key to much of this change. Just a few years ago, many boards were not enthusiastic about the idea of adding a director solely with technology or digital skills. But times are changing. Technology is increasingly becoming a critical skill to have on the board. We consulted our experts in the nine industries we analyzed, and all of them put technology high on the “must-have” list for new directors. Interestingly, financial, operational and industry experience—the top three from our 2016 Annual Corporate Directors Survey, were not among the most commonly listed.
Taking a fresh look
If your company is shifting gears and changing the way it does business, it may be important to take a fresh look at your board composition at more frequent intervals. Some boards use a skills matrix to see what they might be lacking in their board composition. Others may be forced by a shareholder activist to add new skills to the board.
So how do you fill the holes in the backgrounds or skills you want from your directors? One way is to look to other industries. As our analysis shows, board composition and refreshment approaches vary by industry. As industry lines blur, other industry perspectives could compliment your company—it might be helpful to consider filling any holes with board members from other industries.
No matter which approach you take, it’s very important to think about your board’s composition proactively. Use your board evaluations to understand which directors have the necessary skills and expertise—and which might be lacking what the board needs. Think about your board holistically as you think about your company’s future. Your board composition is critical to ensuring your board is effective—and keeping up with the world outside the boardroom.
Appendix
How do our industry peer groups stack up to the S&P 500? Making this evaluation can be a good way to begin determining whether your board has the right balance in terms of board composition.
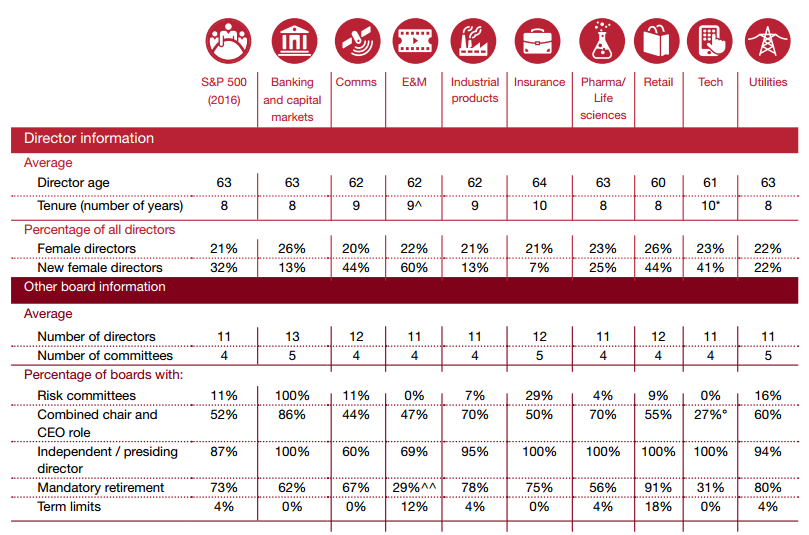
* Analysis excludes two companies that are newer spinoffs.
° Analysis excludes one company that does not combine or separate the roles.
^ Excludes the tenure of one newly-formed company.
^^ Four of the five companies that have a mandatory retirement age have waived or state that the board can choose to waive it.
Sources: Spencer Stuart, U.S. Board Index 2016, November, 2016; PwC analysis of US SEC registrants: 27 of the largest industrial products companies by market capitalization and revenue, May 2016; 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue, May 2016; 21 of the largest banking and capital markets companies by revenue, September 2016; 24 of the largest insurance companies by market capitalization, May 2016; 17 of the largest entertainment and media companies by revenue, May 2016; nine of the largest communications companies by revenue, May 2016; 25 of the largest power and utilities companies by revenue, October 2016; 16 of the largest technology companies by revenue, May 2016; 23 of the largest pharma/life sciences companies by revenue, May 2016.
Endnotes:
1Sources: PwC, 2016 Annual Corporate Directors Survey, October 2016; Spencer Stuart, 2016 US Board Index, November 2016.(go back)
2Sources: PwC analysis of 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 25 of the largest power and utilities companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, October 2016; Spencer Stuart, U.S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
3Sources: PwC analysis of 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 17 of the largest entertainment and media companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
4Sources: PwC analysis of 21 of the largest banking and capital markets companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, September 2016; PwC analysis of 16 of the largest technology companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
5Sources: PwC analysis of US SEC registrants: nine of the largest communications companies by revenue, May 2016; 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue, May 2016; 21 of the largest banking and capital markets companies by revenue, September 2016; 24 of the largest insurance companies by market capitalization, May 2016; 16 of the largest technology companies by revenue, May 2016; 17 of the largest entertainment and media companies by revenue, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, U.S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
6Analysis excludes two companies that are newer spinoffs.(go back)
7Sources: PwC analysis of 16 of the largest technology companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, U.S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
8Sources: PwC analysis of 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 21 of the largest banking and capital markets companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, September 2016; Spencer Stuart, U.S. Board Index 2016, November, 2016(go back)
9Sources: PwC analysis of 17 of the largest entertainment and media companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of nine of the largest communications companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, S. Board Index 2016, November 2016.(go back)
10Sources: PwC analysis of 17 of the largest entertainment and media companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of nine of the largest communications companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; Spencer Stuart, S. Board Index 2016, November 2016; PwC analysis of 11 of the largest retail companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 21 of the largest banking and capital markets companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, September 2016; PwC analysis of 24 of the largest insurance companies by market capitalization that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 16 of the largest technology companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016; PwC analysis of 23 of the largest pharma/life sciences companies by revenue that are also US SEC registrants, May 2016.(go back)
 Print
Print