Robyn Bew is director of strategic content development for the National Association of Corporate Directors (NACD). This post is based on a NACD publication, available here.
In 1996, the Report of the NACD Blue Ribbon Commission on Director Professionalism made recommendations on issues including establishing mechanisms for appropriate director turnover/tenure limitations, evaluation of the full board and of individual directors, and ongoing director education. [1] It stated, “the primary goal of director selection is to nominate individuals who, as a group, offer a range of specialized knowledge, skills, and expertise that can contribute to the successful operation of the company,” and advocated that boards must “[expand] the pool of potential nominees considered to include a more diverse range of qualified candidates who meet established criteria.” [2]
Twenty years later, the world in which boards operate has been transformed in fundamental ways, including increased complexity in the business environment; rapidly changing technology; volatility in global politics as well as in international economic and trade flows; the proliferation of information; the presence of major threats such as cyberattacks; higher levels of engagement between companies, boards, and investors of all stripes, including activists; new regulatory requirements; and greater levels of scrutiny from the press and the public. The velocity of the changes directors are facing shows no signs of slowing down.
The NACD 2016 Blue Ribbon Commission began its dialogue by asking whether boards are keeping up, and concluded that there is no single answer. It is clear that advancing director ages and tenures, coupled with low boardroom turnover, are external symptoms that are of increasing concern to investors and other stakeholders. But equally—if not more—significant is the question of whether a board’s composition, director skill sets, and core board processes remain fit-for-purpose in a world where the board’s mandate is evolving in fundamental ways, including but not limited to earlier involvement in strategy-setting discussions with management and greater engagement between designated board members and major investors. This new mandate places substantially different demands on directors, and boards need to ask themselves, “Are we ready?”
Many stakeholders are focused on encouraging higher levels of director turnover—often termed “board refreshment”—through the use of tenure-limiting mechanisms. We believe that such mechanisms can help to drive needed change in the boardroom, but alone they are not sufficient to ensure that boards truly remain fit for-purpose over time. We are encouraging directors to think more holistically, and more ambitiously. Business as-usual approaches will not be sufficient.
As a starting point, directors should review the organization’s corporate governance guidelines, including the board’s mission and key operating principles. Are all board members familiar with them? How often are they reviewed and updated? How rigorously have they been implemented? Do they help to foster a culture of continuous improvement and ongoing learning?
Boards are unique entities. While (in the case of public companies) they are elected by and accountable to shareholders, they are self-constituting, self-evaluating, self-compensating, and self-perpetuating: that is, in the normal course of business, they control their own composition and succession planning. This also means that boards are equipped to take action to elevate their performance on an entirely self-directed, voluntary basis—and they should do so. Otherwise, if board leadership appears to be passive or slow to act in the face of a challenging competitive environment and greater scrutiny from all angles, directors should prepare for the possibility of “shock treatments” imposed from the outside, in the form of activist challenges, regulatory mandates, or quotas. Put another way, without sufficient and timely evolution, boards could face revolution.
Beyond “Board Refreshment”: Building a Strategic-Asset Board
Too many companies still view changes in their boardrooms as necessary primarily on an incremental basis and from the standpoint of director replacement—i.e., responding to the loss of directors due to age or other reasons for departure in a fairly reactive, one-off manner. And while (as noted above) the idea of “board refreshment” has attracted increasing attention in the corporate governance community, as well as with regulators and the press, in the words of one Commissioner, “the current definition [of board refreshment] can still be somewhat limiting—it can imply change for the sake of change.”
The Commission advocates a more ambitious approach, centered on proactive measures that help to build a strategic-asset board. Characteristics of this approach include:
- A focus on continuous improvement of overall board composition, individual director skills, and boardroom processes—collectively aimed at achieving and maintaining a high-performance board—rather than a primarily reactive or event-driven approach to board change. One indicator of well-established continuous-improvement processes is that they are used in times of good performance, not just when the company is in a down cycle or facing external challenge
- Using the company’s current and future needs as the starting point for determining board composition. Such an approach will certainly include considerations about maintaining an appropriate level of continuity and institutional memory in the boardroom—but in the words of Vanguard CEO Bill McNabb, “To be frank, board members cannot be more worried about their own seats than they are about the future of the company they oversee.” [3]
- A set of tools and processes that works together as a system for continuous improvement—avoiding what one Commissioner called the “formulaic approach” of overreliance on automatic tenure-limiting mechanism
While outcomes will be specific to individual boards, in general, we expect to see improvements such as the following:
- Boards that are composed of directors who collectively have the right skills and insights to support the formulation and execution of the organization’s strategy—in other words, boards where it is clear that the whole is greater than the sum of the parts
- Boards that have the ability to adapt and retool themselves over time, so that they are able to maintain a superior level of oversight and guidance and evolve as the organization’s strategy and competitive environment evolve
- Boards that are transparent in their communications with investors and other stakeholders about who they are and how they operate
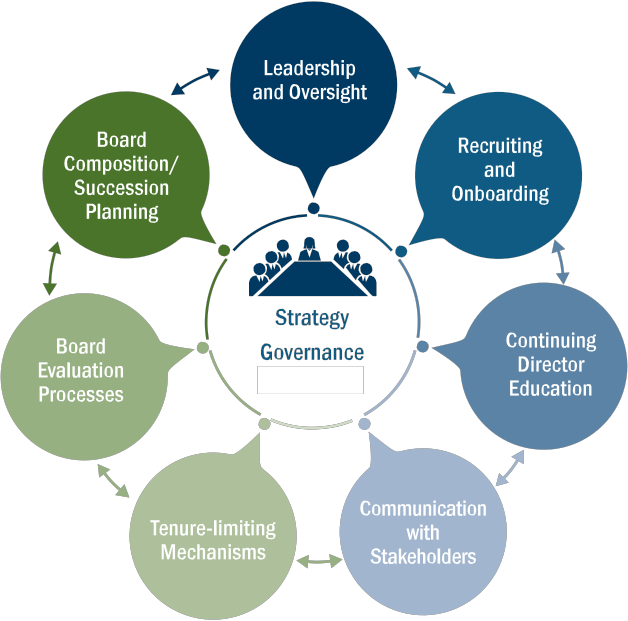
SECTION 1 of the report describes the ways in which the board’s mandate has evolved in response to external factors and strategic imperatives, and outlines the ways in which the Commission believes boards must respond: by moving beyond traditional approaches to “board refreshment” and establishing a system for continuous improvement in the boardroom.
SECTION 2 explores the key dimensions of continuous improvement, focusing on seven areas in particular: board leadership and oversight responsibilities; board composition and succession planning; recruiting and onboarding new directors; processes for board evaluation; continuing education; tenure-limiting mechanisms; and communication with shareholders and stakeholders.
SECTION 3 summarizes the Commission’s recommendations, and the Appendices provide tools and related resources to help boards implement the recommendations.
NACD has characterized the mission of the board as “[becoming] a strategic asset of the company measured by the contributions we make—collectively and individually—to the long-term success of the enterprise.” [4] We believe this report will help directors in organizations of all sizes and in all sectors to do exactly that.
Recommendations of the 2016 NACD Blue Ribbon Commission
- Boards should review their governance principles on a regular basis (at least every other year) to ensure they are complete, up-to-date, and fully understood by current members and director candidates. Governance principles should incorporate a definition of director responsibilities, including a commitment to ongoing learning and the belief that service on the board should not be considered to be a permanent appointment.
- The nominating and governance committee should oversee the board’s processes for continuous improvement, working in close coordination with the nonexecutive chair or lead director and with the endorsement of the full board.
- Director renominations should not be a default decision, but an annual consideration based on a number of factors, including an assessment of current and future skill sets and leadership styles that are needed on the board.
- Nominating and governance committees should develop a “clean-sheet” assessment of the board’s needs in terms of director skill sets and experience at least every two to three years, and use it as an input in continuous-improvement efforts (including recruitment and director education).
- The director recruitment process should have a time horizon that matches the organization’s long-term strategy, typically three to five years or more. The process should be designed to include candidates from diverse backgrounds.
- Recruiting and onboarding processes should familiarize prospective and new directors with the board’s governance principles and set expectations regarding criteria for renomination, ongoing director education, and other aspects of continuous improvement as defined by the board.
- Conduct annual evaluations at the full-board level, and evaluations of committees and individual directors at least once every two years. Use a qualified independent third party on a periodic basis, to encourage candor and add a neutral perspective.
- Participation in continuing education should be a requirement for all directors, regardless of experience level or length of board tenure.
- Tenure is an important aspect of boardroom diversity. Nominating and governance committees should strive for a mix of tenures on the board—for example, maintaining a composition that includes at least one director with <5, 5–10, and >10 years of service.
- High-performance boards will not need to rely exclusively on tenure-limiting mechanisms to ensure appropriate board turnover and composition. However, boards that use such policies should consider replacing or combining retirement age with a maximum term of service.
- Communications with investors and other key stakeholders should include a detailed explanation of the link between the organization’s strategic needs and the board’s composition and skill sets, as well as information about the board’s continuous-improvement processes.
Tools for Directors
The report’s 12 appendices enable boards to benchmark their current practices and implement the report’s recommendations. Examples of appendix content are below.
Early Engagement: Going Beyond Traditional Board Succession Planning
A reference list of more than 25 questions to help directors evaluate
- the board’s ability to manage succession planning as a portfolio, instead of as a series of one-off replacements of individual directors;
- the strength of the board’s search capabilities, including early-engagement activities and the depth of the candidate pipeline; and
- the role that board and company culture play in succession planning.
Considerations for Upgrading Board Evaluation Processes
The appendix provides guidance to help boards
- establish effective, ongoing rhythms for evaluation processes;
- avoid “evaluation fatigue”;
- inform the use of third-party facilitators;
- make evaluations more holistic by incorporating input from management; and
- act on evaluation results.
Guidelines for Developing Board and Individual-Director Learning Agendas
The appendix includes frameworks and questions to help inform full-board and individual-director education activities:
- Suggested categories and topic areas for education, with sourcing strategies
- A personal learning and development checklist for directors
- Outline of a “lifecycle approach” to learning and development for the board, with components of a global director leadership profile
Tools, Templates, and Examples
- Multiyear board succession planning matrix
- Sample board and committee-level evaluation questions
- New-director onboarding checklist
- Examples of effective disclosures of director skills, board evaluations, and director education
- Examples of corporate governance principles and board tenure policies
* * *
The complete publication is available exclusively to NACD members and is available for download here.
Endnotes:
1NACD, Report of the Blue Ribbon Commission on Director Professionalism, 2011 ed. (Washington, DC: NACD, 2011), pp. 12, 5, 15, 10.(go back)
2Ibid., p. 13.(go back)
3F. William McNabb III, Getting to Know You: The Case for Significant Shareholder Engagement, Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance and Financial Regulation, June 24, 2015.(go back)
4NACD, Report of the Blue Ribbon Commission on Board Evaluation: Improving Director Effectiveness, 3rd ed. (Washington, DC: NACD, 2010), p. 2.(go back)
 Print
Print