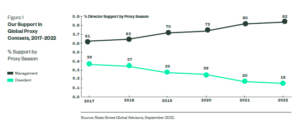
Our approach to nominee selection reflects our belief that strong, independent, and effective boards underpin value creation at companies in which we invest. On behalf of the company’s shareholders, Boards: 1) oversee management; 2) provide guidance on strategic matters; 3) select the CEO and other senior executives; 4) create a succession plan for the board and management; 5) provide risk oversight; and, 6) assess the performance of the management team.
As previously emphasized, nominating committees that comprise independent directors are best placed to assess which individuals can properly fulfill these duties, and act as effective fiduciaries. As long-term shareholders, we vote for members of the board, including nominating committee members, who play a critical role in determining board composition. While our default position is to support the committees’ judgement, we consider the following factors when evaluating dissident nominees:
- Strategy presented by dissident nominees versus that of current management, as overseen by the incumbent board
- Effectiveness, quality, and experience of the management slate
- Material governance failures and the level of responsiveness to shareholder concerns and market signals by the incumbent board
- Sustained company underperformance and lack of a compelling recovery plan
- History of both company and activist shareholder engagement cultures
Universal Proxy
Starting August 31, 2022, the use of universal proxy cards is now required in all non-exempt director election contests at publicly-traded companies in the US. The changes are as follows:
- Shareholders voting by proxy in contested elections have the same flexibility in voting for directors as shareholders who physically attend and vote at the shareholder meeting
- All shareholders have the ability to vote for a combination of director nominees from competing slates, gaining the ability to “mix and match” for the first time
- The minimum share ownership required for shareholders to nominate a director to the board has been significantly lowered, decreasing associated costs and barriers to entry
Academic evidence has indicated this change will not systemically favor either activist shareholders or incumbent boards. As such, we welcome this development, since it has the potential to strengthen shareholder voice and may lead to more balanced vote outcomes.
Nonetheless, we will carefully monitor evidence of an increase in the following possible outcomes, as well as their potential unintended consequences:
- Settlements between activist shareholders and companies, with board seats used as bargaining chips
- Proxy campaigns used in place of shareholder proposals to further a broader set of topics of interest to shareholders
- Contested elections due to decreased cost and lower barriers to entry
As long-term investors in portfolio companies on behalf of our clients, we will remain invested well after dissident directors leave the board and short-term investors exit the stock. We believe that leveraging board seats as bargaining chips diminishes shareholder democracy. This also mutes our opportunity to advocate for a company’s long-term performance that aligns with our clients’ interests.
Upholding Shareholder Democracy
Despite improvement in shareholder engagement, companies are increasingly engaging in entrenchment tactics that circumvent shareholder voice and the democratic process. These developments come against the backdrop of recent market volatility, the global pandemic, and inflationary concerns. Such practices include, but are not limited to:
- Entering into preferred financing agreements that require investors to vote their shares in line with all management proposals
- Establishing new special voting class shares (e.g., “Founder’s shares”) well after the company has gone public
- Failing to provide sufficient disclosure that explains compelling rationale behind changes to shareholder rights, capital allocation, and/or governance structure
- Refusing to engage constructively with shareholders regarding board composition, shareholder rights, or competitive offers to buy the company and/or its assets
- Adopting shareholder rights plans (“poison pills”) with no time-bound limits and/or compelling rationale
Unsurprisingly, these company actions are often cited by activist shareholders in their argument for board refreshment. Through our engagement with portfolio companies and activist shareholders, we will continue to apply close scrutiny to the practices above.
Supporting Investor Choice on Proxy Voting
We are supportive of giving our clients greater choice around how their shares are voted. Today, clients invested through our separately managed account structures have the option to retain proxy voting authority over the securities held in their accounts that we manage for them. We are continuing to explore the possibility of providing investor choice to more products and client types.
In parallel with this client offering, some policymakers have proposed new measures that intend to further empower individual investors. While we are supportive of the spirit of these legislative proposals, we are concerned by possible unintended consequences, including:
- Amplifying the voting influence of select shareholders, such as activists with short-term interests, those outsourcing responsibility to proxy research advisors, and company insiders
- Creating challenges for companies to reach a voting quorum
- Diminishing the opportunity for clients to benefit from the experience of institutional investors in exercising a long-term perspective in voting decisions
The Long-Term Shareholder Provides a Stabilizing Voice
In an environment increasingly defined by market volatility and the outsized influence of a few short-term oriented actors, long-term shareholders play a unique and important role. Shareholders focused on maximizing long-term value creation and sound corporate governance practices – a precondition for long-term performance – are more important than ever. Indeed, when making any significant decisions relating to capital allocation and long-term strategy, particularly those with voting implications, companies can benefit from soliciting and considering the long-term shareholder voice in this process.
Investors with long-term horizons, sufficient resources, and productive relationships with their portfolio companies are ideally positioned to deliver value for their clients. These stewards of capital can advocate for enhanced governance practices and risk mitigation of financially material issues, and keep companies focused on long-term strategy.
For these reasons, defensive company entrenchment tactics, last-minute settlements with activist shareholders, and evolving legislative environments all have the potential to cause adverse effects on constructive engagement – silencing the voice of long-term shareholders and potentially upending shareholder democracy. This outcome would be detrimental to the critical role that effective boards – who are elected by shareholders to represent their interests – play in keeping management focused on the long-term goals of their companies.
Conclusion: Bridging the Time-Horizon Gap
The diverse investment philosophies among capital markets participants represent an inherent mismatch between investors with short and long-term time horizons. As a long-term investor, and stabilizing presence for our portfolio companies, we provide a consistent and constructive voice to portfolio companies through our voting and engagement activities.
While our quasi-permanent holding period may differ from that of activist shareholders, enhancing long-term value creation at companies that we both own is a mutually beneficial goal. Boards and management teams can bridge the gap between short and long-term interests by remaining focused on managing material risks and emerging opportunities.
Activist shareholders can better build consensus among voting shareholders by nominating dissident directors focused on long-term strategy and value creation. Generally, director nominees who serve as responsible stewards by fulfilling their fiduciary duty will more likely have the support of long-term shareholders.
At State Street Global Advisors, we will continue to serve as a constructive partner to our portfolio companies and a consistent voice to their boards and management teams. In contested elections, we will continue to engage with both companies and activist shareholders, giving stronger consideration to approaches that bridge short and long-term interests. This will effectively improve long-term, risk-adjusted returns, well after activist shareholders exit an investment.
While there may always be an inherent divergence between investors with short and long-term objectives, we believe that healthy competition, constructive dialogue, and transparent debate fuel shareholder democracy. As such, resisting any efforts to disenfranchise the voice of long-term shareholders will benefit the average investor, who has benefited greatly from the development of strong and efficient capital markets.
The complete memorandum is available here.
Endnotes
1“Why Index Investing is Good for Markets – And Investors”. State Street Global Advisors. (August 2019)
https://www.ssga.com/investment-topics/environmental-social-governance/2019/10/why-index-investing-is-good-for-markets.pdf (go back)
2Brav, Alon. Jiang, Wei and Kim, Hyunseob. ”The Real Effects of Hedge Fund Activism: Productivity, Asset Allocation, and Labor Outcomes” Oxford University Financial Review. (June 2015) http://rfs.oxfordjournals.org/content/28/10/2723.full.pdf (go back)
3“H1 2022 Review of Shareholder Activism”, Lazard Capital Markets Advisory Group. (July 2022)
H1 2022 Review of Shareholder Activism (lazard.com) (go back)
4“Shareholder Activism in 2021” Insightia. (January 2022) (go back)
5Gonzalez, Juan Pablo, Goodman, Anthony, van Biesen, Tanya, Olson, Nels. “The Return of the Activist Investor” Korn Ferry (August 2022) https://www.kornferry.com/insights/this-week-in-leadership/the-return-of-the-activist-investor (go back)
6State Street Global Advisors Voting Data as of date 8/1/2022 (go back)
7“The Effect of Shareholder Activism on Corporate Strategy”, Spencer Stuart, Evercore & NYSE Governance Services. (April 2016) https://www.spencerstuart.com/research-and-insight/the-effect-of-shareholder-activism-on-corporate-strategy (go back)
8“Global Proxy Voting and Engagement Guidelines” State Street Global Advisors. (March 2022).(go back)
9“Fact Sheet: Universal Proxy Rules for Director Elections”, U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. (July 2022)
https://www.sec.gov/files/34-93596-fact-sheet.pdf (go back)
10Hirst, Scott. “Comment Letter to SEC: Universal Proxy”. (June 7, 2021) https://www.sec.gov/comments/s7-24-16/s72416-8893542-241143.pdf (go back)
11Hirst, Scott. “Universal Proxies”. Yale Journal on Regulation. Vol 35, No.2. (September 25, 2017)
https://ssrn.com/abstract=2805136 (go back)
12“The Activist Report: 13D Monitor. 10 Questions with Ben Colton”, 13D Monitor. (February 2022) (go back)
13Liekefett, Kai H.E. “Welcoming the Universal Proxy”, Sidley (July 2022) https://www.sidley.com/-/media/publications/welcoming-the-universal-proxy.pdf?la=en (go back)
14Bebchuk, Lucian A. and Brav, Alon and Jiang, Wei and Keusch, Thomas, “Dancing with Activists” (June 1, 2017). Journal of Financial Economics, Harvard Law, Columbia Business School and European Corporate Governance Institute.
https://ssrn.com/abstract=2948869 (go back)