Ali Saribas is a Partner, and Carmen Ng is a Director at SquareWell Partners. This post is based on their SquareWell memorandum.
i. Introduction
SquareWell published the inaugural edition of “What do Shareholders Propose“, a comprehensive review of all shareholder proposals related to environmental, social, and governance (“ESG”) topics in Europe and the United States for 2022 and 2023, including the “Anti-ESG” movement. The full paper can be downloaded from here.
Broadly speaking, shareholder proposals can either focus on “values” or “value.” However, the distinction between the two has become increasingly blurred over the years. The study aims to understand the transatlantic differences in proposals filed and voted on by shareholders on topics related to their values on “ESG” issues at the AGMs of S&P 500 and STOXX Europe 600 companies.
In 2023, a record 490 “Pro-ESG” shareholder proposals were filed across the S&P 500 and STOXX Europe 600 indices, marking an 8 percent year-on-year increase. However, the adoption rate for such proposals at S&P 500 companies halved to 5.4 percent compared to 2022. Additionally, no “Pro-ESG” proposals passed at STOXX Europe 600 companies in 2023.
In the United States, the number of “Anti-ESG” proposals surged by 64 percent in 2023, overshadowing the 10 percent increase in “Pro-ESG” shareholder proposals. The surge in shareholder proposals is fueling mounting frustration among companies with the existing SEC “No-Action” process, which has facilitated a higher influx of shareholder proposal submissions. The lawsuit initiated by ExxonMobil against Follow This, seeking to impede a resolution put forth by the NGO in 2024, reflects this growing discontent.
In Europe, the number of shareholder proposals on “ESG” topics and average shareholder support remained consistent compared to 2022, displaying a different dynamic compared to the contrasting trends observed in the United States.
Early data from 2024 suggests a reversal in trends. Between January and April 2024, shareholder proposals on “ESG” topics filed at S&P 500 companies dropped by nearly 40 percent compared to the same period in 2023, marking a departure from the record-high volumes observed in 2022 and 2023. Notably, there have been fewer social and governance proposals, with social proposals decreasing by a quarter and governance proposals being halved. Proposals related to environmental topics remain relatively stable.
ii. E&S proposals correlate to risk
Environmental and social shareholder proposals are closely tied to sector-specific material issues (Figure 1). For instance, “Climate” proposals predominantly focus on companies operating in the Energy and Financials sectors, while “Human Rights” proposals tend to be concentrated among companies within the Consumer Staples sector. Similarly, “Digital Rights” proposals are exclusively aimed at companies in the Communication Services, Consumer Discretionary, and Information Technology sectors, while “Public Health” proposals are primarily directed at companies in the Health Care, Consumer Staples, and Consumer Discretionary sectors.
This responsiveness to sector-specific concerns is also indicative of the evolving nature of shareholder priorities. Between January and April 2023, there were several proposals related to access to medicine and COVID-19 vaccines at S&P 500 companies yet absent during the same period in 2024. This shift underscores how shareholder activism is sensitive to current events and evolving societal concerns, shaping the trajectory of discussions over time.
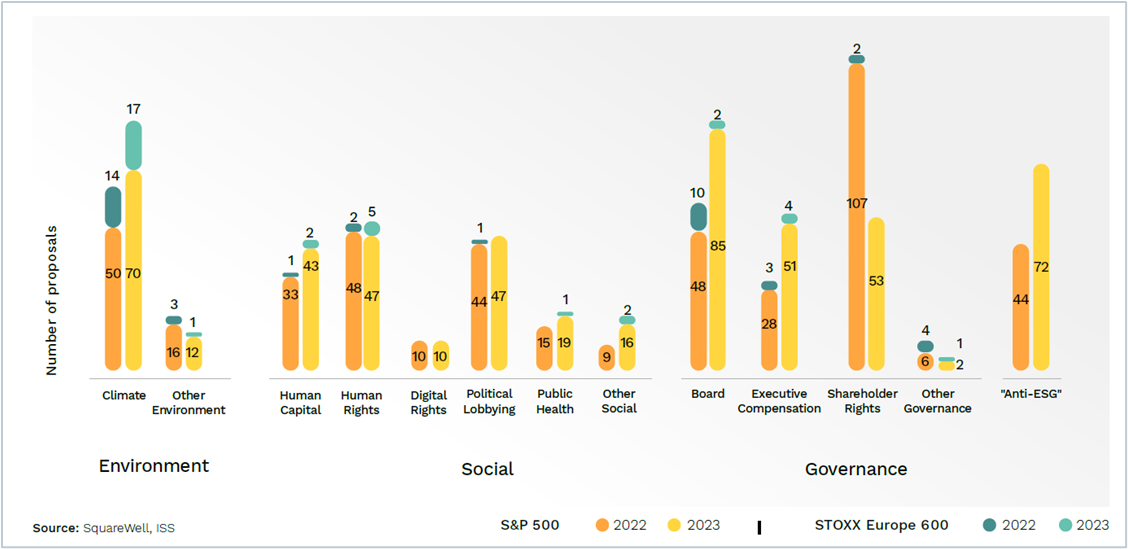
In 2023, the three most prevalent shareholder proposals at S&P 500 companies were related to “Board,” “Anti-ESG,” and “Climate,” with shareholder proposals related to “Shareholder Rights” being the most prevalent in 2022. At STOXX Europe 600, the predominant sub-category related to shareholder proposals on “Climate,” consistent with the pattern observed in 2022 (Figure 2).
The 2024 season has seen an array of new requests: pharmacies and tobacco companies have been asked to report on cigarette waste, while food and beverage companies face biodiversity proposals to assess their nature-related risks and opportunities. Additionally, there is a growing demand for tech and media companies to publish Artificial Intelligence (AI) transparency reports. Notably, the U.S. union fund AFL-CIO submitted AI proposals at five major companies, including Apple, Comcast, Disney, Netflix, and Warner Brothers Discovery. Among these, the shareholder proposal at Apple garnered 38 percent support from prominent investors such as Norges Bank Investment Management and Legal & General Investment Management. The AI proposals at Disney and Comcast were withdrawn after the companies agreed to enhancing their disclosures regarding the ethical use of AI.
This surge in AI-related proposals reflects the increasing prevalence of AI technology and the growing awareness of its potential risks and impacts. Concerns about AI ethics, biases, privacy, and equality are gaining prominence among investors, highlighting the growing significance of AI-related considerations in corporate governance discussions. Investors are now scrutinizing whether companies are effectively utilizing AI and managing associated risks, and if they have adequate policies and processes to address both the risks and opportunities. Similar to climate issues, there is a rising emphasis on ensuring a “just transition to AI.” A new ICGN paper provides insights into how investors can effectively engage with portfolio companies regarding AI.
Figure 1 – Number of Environmental & Social Proposals by Sector and Subcategories in 2023
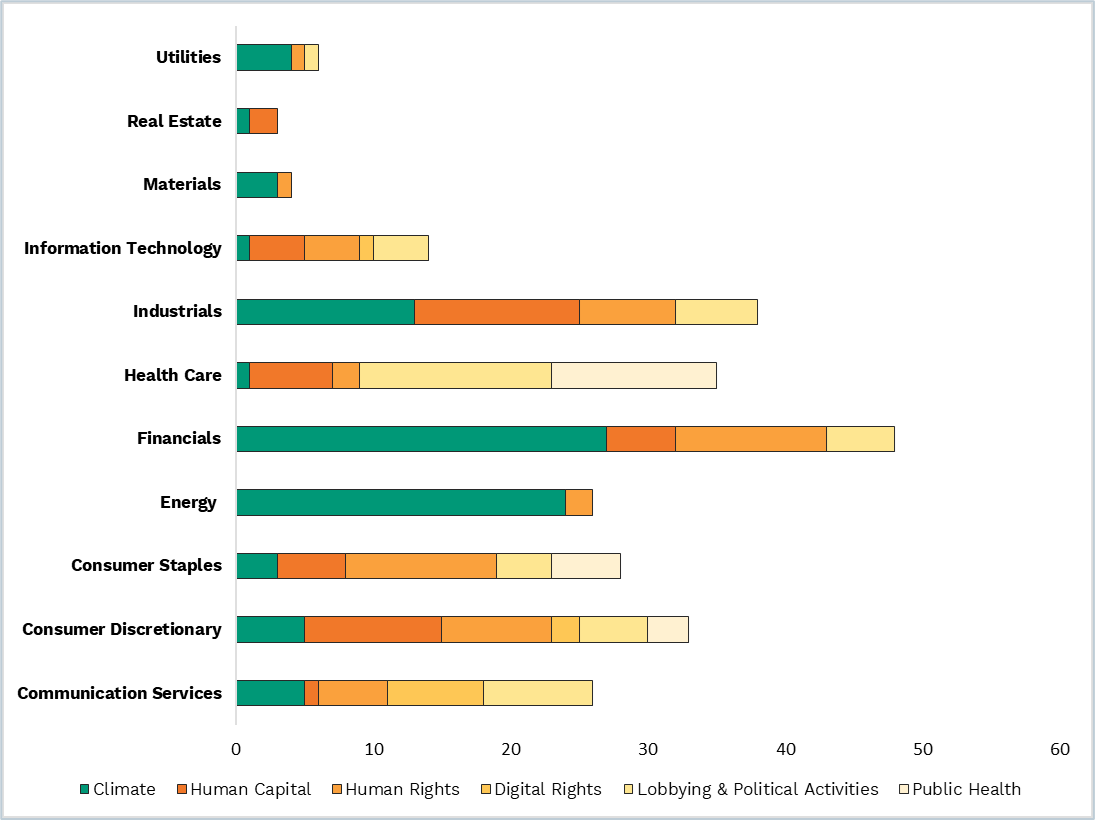
Figure 2 – Number of Shareholder Proposals by Sub-Categories, 2022-2023
iii. European and American investors divided on issues
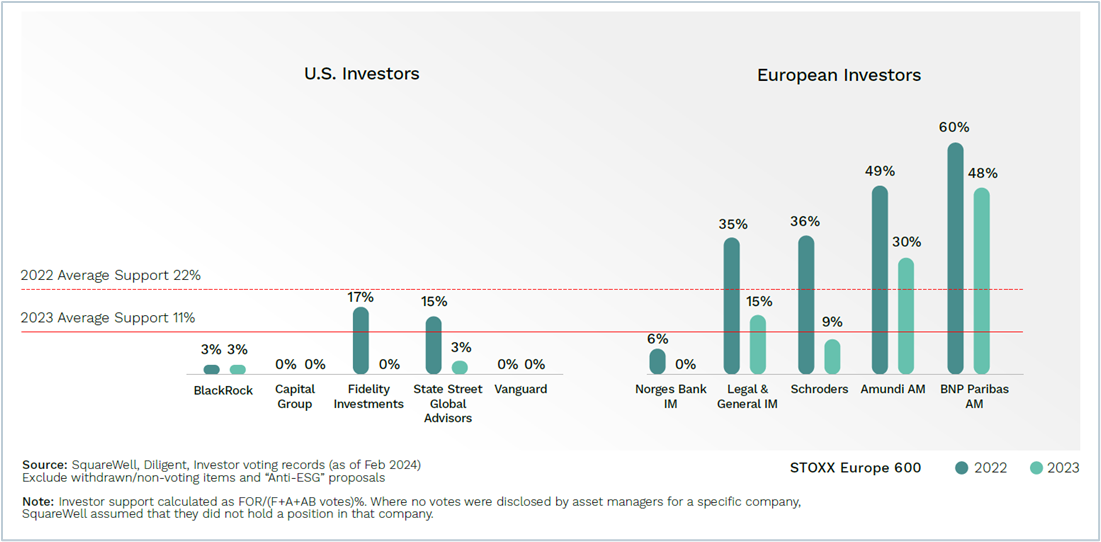
European investors exhibited stronger support for “Pro-ESG” proposals, with the five large European asset managers supporting three quarters of proposals at the S&P 500, versus the five large U.S. asset managers who averaged just 12 percent. In the STOXX 600, European investor support was one-fifth, versus U.S. investor support of 1 percent. (Figure 3 and 4)
The disparity between European and American investors can be partly attributed to the inclusion in the U.S. peer group for this analysis of the three major passive American investors—BlackRock, Vanguard, and State Street Global Advisors—who are known to be more “management friendly”. Specifically, Vanguard supported only 4 percent of the shareholder proposals related to “Pro-ESG” in 2023, and BlackRock supported only 5 percent.
This echoes AQTION’s article for Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance, that European investors have demonstrated a proportionally higher endorsement of environmental and social initiatives compared to their counterparts in the United States. While climate initiatives enjoy broad support, European investors appear to be taking the lead in supporting initiatives relating to biodiversity and social topics.
Moreover, European investors tend to favor stewardship teams making decisions with significant input from fund managers, a practice less common among US investors. This bridging of the gap between “values” and “value” is further propelled by a regulatory environment in Europe that strongly promotes “ESG” principles, exemplified by EU policies such as the Sustainable Finance Action Plan and the EU Taxonomy. This regulatory framework is underpinned by higher social expectations regarding environmental and social issues, including labor rights, gender diversity, and climate action.
Figure 3 – Investors’ Support for “Pro-ESG” Shareholder Proposals at S&P 500 Companies
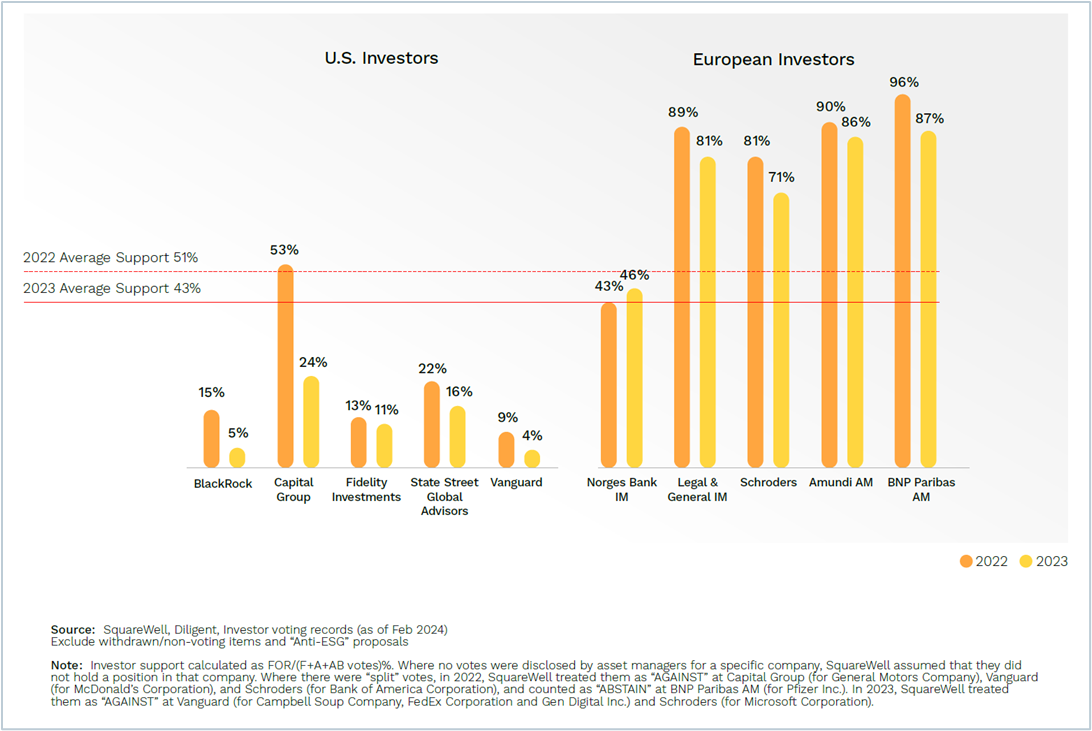
Figure 4 – Investors’ Support for “Pro-ESG” Shareholder Proposals at STOXX 600 Companies
iv. Proxy Advisors split the Atlantic divide
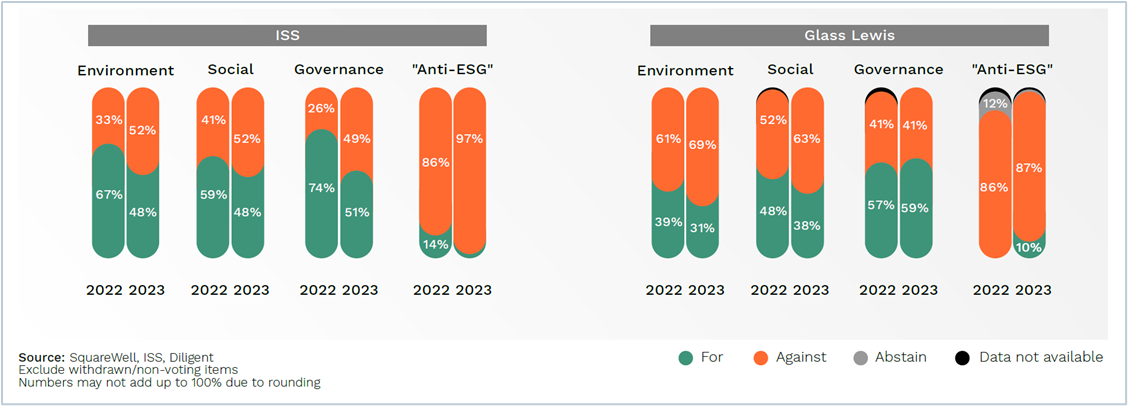
ISS and Glass Lewis supported nearly half of “Pro-ESG” proposals, taking the middle ground between the largest U.S. investors (support for 1 in 10), and the largest European investors (supporting nearly three-quarters). Between the two proxy advisors, Glass Lewis demonstrated lower support for shareholder proposals in both 2022 and 2023, compared to ISS (Figure 5 and 6).
S&P 500
In 2023, ISS supported 43 percent of 515 proposals, while Glass Lewis backed 41 percent. Notably, ISS’s support dropped by 19 percentage points from 2022.
Both ISS and Glass Lewis consistently supported proposals relating to “Board Skills and Diversity”, “Equal Voting Rights”, “Methane”, and “Digital Privacy & Civil Rights Risks”. They consistently oppose proposals on “CEO/Worker Pay Ratio”, “Climate Risk in Retirement Plans”, “Workers’ Rights in Supply Chain”, “Antimicrobial Resistance” and “Tobacco” proposals.
ISS reduced its support for “Anti-ESG” proposals, backing only two in 2023 compared to six in 2022. Meanwhile, Glass Lewis increased its support to seven, having supported none in 2022. All “Anti-ESG” proposals supported by proxy advisors in 2023 are those requesting companies to have an independent board chair. These shareholder proposals, often disguised as calls for good governance, also garnered support from large investors.
The growing “Anti-ESG” sentiments in the U.S. have also led ISS to develop a new “ESG skeptic” policy in partnership with Bowyer Research for investors seeking to “depoliticize” their approach. Initially, the policy will be offered only to public pension funds.
Figure 5 – Proxy Advisors’ Vote Recommendations on Shareholder Proposals, S&P 500
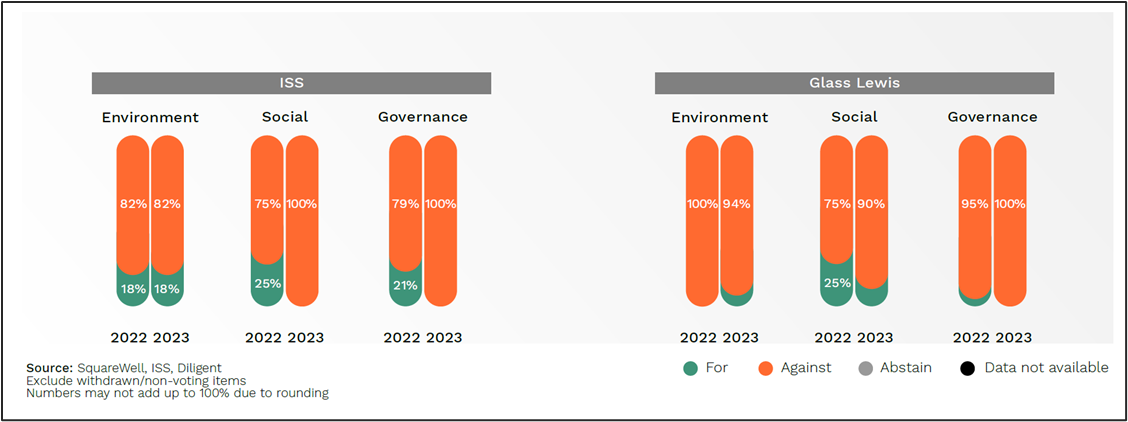
STOXX Europe 600
In 2022 and 2023, ISS supported only 11 out of 73 shareholder proposals that went to a vote (15 percent), while Glass Lewis supported even fewer, backing only four shareholder proposals (5 percent).
Notably, ISS did not endorse any shareholder proposals related to social and governance topics in 2023. Instead, all three shareholder proposals supported by ISS were climate-related, including the “Say on Climate” proposal at Glencore which was also supported by Glass Lewis.
Glencore’s proposal received 29 percent support including from State Street Global Advisors, Legal & General Investment Management, Schroders, and Amundi Asset Management. Among the investor sample in our study, we observed a substantial rise to around 40 percent in average shareholder support when both ISS and Glass Lewis recommend “FOR” a proposal and a sharp decline to around 8 percent when both advisors recommended “AGAINST”
Figure 6 – Proxy Advisors’ Vote Recommendations on Shareholder Proposals, STOXX Europe 600
v. Concluding Thoughts
The examination of shareholder proposals across Europe and the United States unveils a nuanced landscape shaped by regional disparities, regulatory frameworks, and shifting investor preferences.
While European investors demonstrate stronger support for “ESG” initiatives compared to their American counterparts, driven by regulatory frameworks and higher social expectations, the United States grapples with a surge in “Anti-ESG” sentiments and a growing polarized political landscape.
Looking ahead, we anticipate continued evolution in shareholder activism, as companies navigate the complexities of “ESG” considerations, regulatory and political landscapes, and investor expectations to drive sustainable corporate practices that creates value (and not focused solely on “values”).
 Print
Print